Abstract
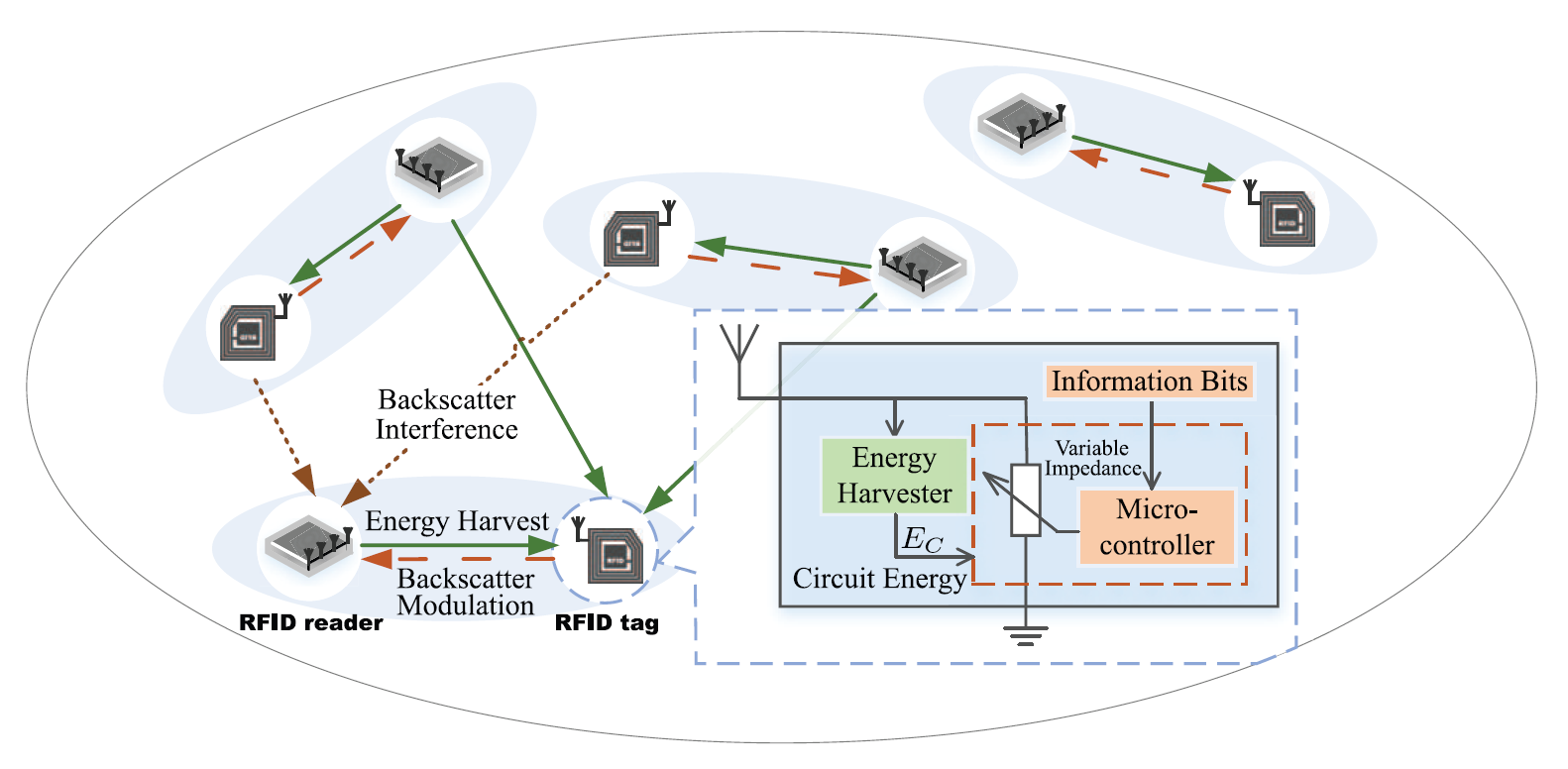
In the fifth generation era, the pervasive applications of Internet of Things and massive machine-type communications have initiated increasing research interests on the backscatter wireless powered communication (B-WPC) technique due to its ultrahigh energy efficiency and low cost. The ubiquitous B-WPC network is characterized by nodes with dynamic spatial positions and sporadic short packets, of which the performance has not been fully investigated. In this paper, we give a comprehensive analysis of a multi-antenna B-WPC network with sporadic short packets under a stochastic geometry framework. By exploiting a time-space Poisson point process model, the behavior of the network is well captured in a decentralized and asynchronous transmission way. We then analyze the energy and information outage performance in the energy harvest and backscatter modulation phases of the backscatter network, respectively. The optimal transmission slot length and division are obtained by maximizing the network-wide spatial throughput. Moreover, we find an interesting result that there exists the optimal tradeoff between the durations of the energy harvest and backscatter modulation phases for spatial throughput maximization. Numerical results are demonstrated to verify our analytical findings and show that this tradeoff region gets shrunk when the outage constraints become more stringent.